Search Engine Positioning Improvement - Jump to the top of Google
May 2, 2025

Introduction to Search Engine Positioning Improvement
Search Engine Positioning (or Search Engine Position Improvement) is a subset of an overall SEO Strategy. In the following post, we'll talk about the best ways to optimize your web page for higher rankings via content optimization, mobile optimization, SEO analytics, technical SEO and much more. Read on for all the information you will ever need on improving your positions in the search engine rankings.
Search Engine Positioning Improvement vs Search Engine Optimization
.webp)
Unlike some higher level SEO strategies, Search Engine Positioning is not focusing on your site as a whole, or keyword planning, or content clustering. Search Engine Positioning focuses on one or two pages that you have already published and trying to get those to rank as high as possible.
Why does Search Engine Positioning matter?
It's pretty clear and known that the higher you rank in the SERPs (Search Engine Results Page), the higher the CTR (Click Through Rate).
Position 1 vs position 5 could mean the difference between 500 click throughs per month vs 5,000 click throughs per month.
Now image that you have a sales page or a sign up page that has an average conversion rate of 5%. That means that at position 5 in the SERPs you are acquiring 25 (500 click throughs x 5% conversion) new clients a month from your sales page. If you now get your page to position one in the SERPs, you are getting 250 new clients (5,000 click throughs x 5% conversion). That's a huge amount of new customers.
Why is Search Engine Positioning Crucial?
Website Visibility
Per above, the position of your page in the SERPs matters. It matters a lot.
Your websites visibility in Google is a total of the amount of keywords you rank for, their position in the SERPs and the monthly search volume for that keyword.
Increased Organic Traffic
SEO is the long game. It gives you clicks to your site for free while you sleep.
Social Media posts can drive short term traffic spikes, but SEO is where the long term gains are.
You need the most important pages on your website to be higher in the rankings. Page one of Google in fact. If they aren't, that's a very good place to start content optimization to get them there. The higher in the rankings your pages go, the more traffic you get. It's as simple as that.
Your website may be the best in it's domain in the world. You may be solving problems that nobody else has. Without traffic, none of that matters.
It's like having the best dressed window display of all of the shops in your town. If no one walks past your shop, it doesn't matter.
Core Strategies for Effective Search Engine Positioning
We'll dive in to how to identify which pages to optimize further down, but for now let's assume you already know which pages you want to rank for and talk about how to improve their rankings.
Optimizing Page Titles and Meta Descriptions
The key search term that you were part of your initial SEO strategies may not be what your page ends up ranking for.
I've seen many examples of well optimized pages for "X" that end up ranking very well for "Y". If "Y" has search volume and you are in position 11 on the Google SERPs, let's explicitly try to rank for that and move up to position 1.
Switching a page on your website to target another keyword (whilst ensuring that keyword is semantically related to the content on the page and matches the users intent) will involve performing basic on page SEO.
You will want to ensure that this new keyword appears in the Title of the page and the Meta Description. That's SEO strategies 101. You are trying to optimize for the new keyword, so you need to cover those basics at the very start.
Make sure that your new title and meta description are matching the users intent for the new keyword.
High-quality and relevant content

Google rewards quality content and punishes "thin", generic and bad content. Google wouldn't last long if they were sending it's customers to websites that didn't answer the questions they were asking.
Google has it's own methods of understanding from parsing your webpage if the quality is good and will have a good idea of if there has been a good amount of effort put in to creating that content.
The second signal to Google however is if the user likes your content.
If out of 100 people that click through to your page, 99 of them return to Google within 3 seconds and look for another link, that's a pretty good sign that your page did not answer the question or was just a terrible user experience.
Make your content engaging, original and with a personal touch. Also, I can not stress this enough, make sure you are matching the users intent. If they are asking "How to tie a shoe lace" and you are showing a webpage with "Shoelaces for sale", you are not going to be in the SERPs for very long.
SEO trends change, but there are a few concepts within SEO that have never changed, and creating good solid content is one of those.
Internal Linking
Google trusts a website that has good coverage of a topic.
If you want to rank for a page on "Best hairstyles for a Labrador", it would be a good idea to also have articles for "Best hairstyles for a Labradoodle", "Best hairstyles for a French Bulldog" etc. This is called Topical Authority.
Once you have built this topical authority and covered in detail (at a high quality), you will start to attract backlinks to certain pages.
Now, if you get a backlink to "Best Hairstyles for a Pug" and then internally link that article to "Best Hairstyles for a Labrador", you will pass on some of that "link juice" from the Pug to the Labrador page. This internal linking strategy gives you a way to not only tell Google all about your topical authority on a subject, but it also passes that trust that your Pug page got to the Labrador page as well.
Dog hairstyles aside, internal linking really is one of the most important aspects of technical SEO.
Technical SEO for Better Positioning

We've spoken about content structure and content quality, now let's talk about technical SEO, website performance and mobile optimization. The nerdy stuff.
An overview of Technical SEO
Improving Core Web Vitals
Core web vitals cover are based on how you page works in the real world. This is a real in depth subject all by itself, but for the sake of improving your search engine position, let's look go through an overview.
Core web vitals cover three major things:
- Page Speed
- Interactivity
- Visual Stability
These technical aspects are vital in your SEO plan.
Page Speed:
Let's think about Page Speed. There are two major reasons that Page Speed is important:
- Users have a short attention span. If your page takes too long to load, they will back out and go somewhere else.
- Google (and other Search Engines) have a huge amount of pages across the web to index. An unimaginable amount and that amount is getting larger by the minute. If your website is slow and takes a long time to load, they will visit your site less as it costs them more.
When you think about Page Speed in those terms, it's clear that a fast loading page will affect your SEO and therefore your ranking.s
Interactivity:
Have you heard about "rage clicks"? This is when users furiously click and click on a button. This can be caused by a lot of things, but slow to respond UIs are one of the major causes.
If your site scrolls slowly, loads images slowly, takes a long time to move from page to page, gives no user feedback when a button is clicked. All of these things are bad for the user experience and will ultimately be punished by Google.
If you are using a CMS (WordPress or similar), make sure you are using a fast one. Go easy on the plugins, ensure images are compressed, lazy load videos, minify CSS and Javascript. Do as much as you can to make your site as performant and good to use as possible.
Visual Stability:
This one is subtle, but I can bet you'd recognise a website that isn't visually stable.
Image that a page is loading. You see the button that you want to click, and as you go to click it, something above it loads and sends your button shooting downwards. You've now clicked somewhere completely different. Now this may be harmless, it may not be. It's definitely frustrating.
In technical terms, this is measure as "Cumulative Layout Shift". It's a measurement of how predictable and repeatable your page load is.
Just like in life, being stable matters.
Don't forget core web vitals. They often come too low in content creators priority list and get overlooked. If you and another website have similar content with similar on page SEO, your competitive advantage will be your solid core web vitals.
Mobile Optimizations

Google still has 94% of the mobile search market, and whilst it's hard to get exact data on how many of the 16.4 Billion Searches per day are from mobile, it's safe to say it's a lot. At the conservative level, I'd say the split must be around 50/50, meaning 8 Billion per day. Even if was only 10% of total searches, that would still be 1.6 billion searches on mobile a day. These are not numbers to ignore, and Google certainly does not.
If your page is ranking quite well but is not optimized for mobile, fix that, fast. Mobile optimization might be the exact thing you need to boost your page rankings in the search engines.
Keyword Research and Content Optimization
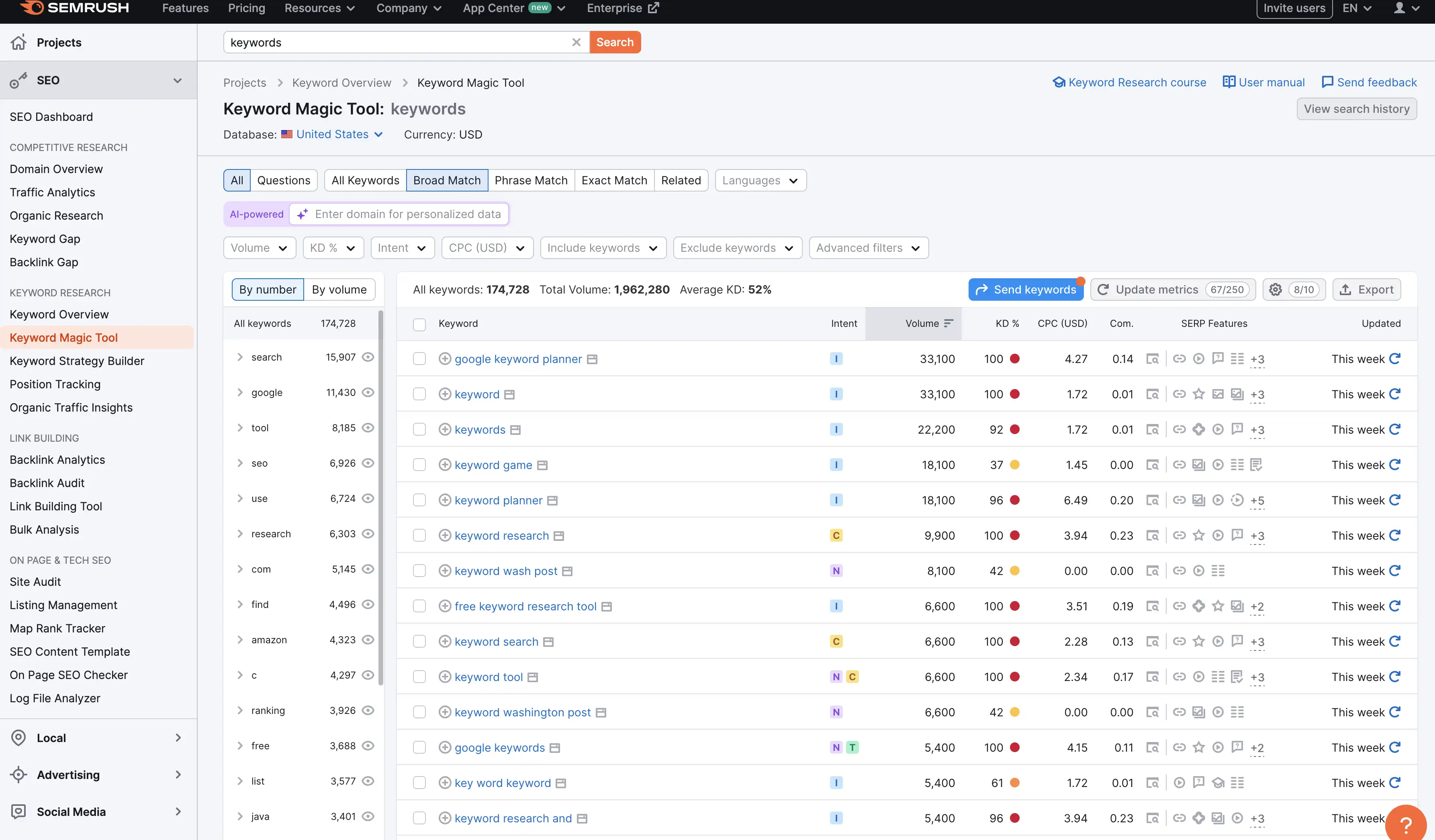
Just as in other SEO Strategies, keyword research plays a major role. It's all well and good identifying that a page of yours is quite high in the rankings for a search term, but of that search term has no search volume, there's no point in ranking for it.
Do your keyword research, check the "Keyword Difficulty", look at the sites about you in the rankings and see if your likely to be able to beat them with some content optimization, a few extra backlinks and some on page SEO. If everyone above you is a heavy duty site (Amazon, Wikipedia, Reddit), chances are that even with the best SEO strategies, you aren't moving up the rankings.
As I preach regularly on this site, we hear at SmoothSEO will always try to remind you that your page has to match the user intent. If you are moving to a new keyword but not matching the intent of the user, Google will quickly realize this and push you down the rankings.
Create content that aligns with what the user is expecting and wanting.
If you match the user intent, organic traffic will come.
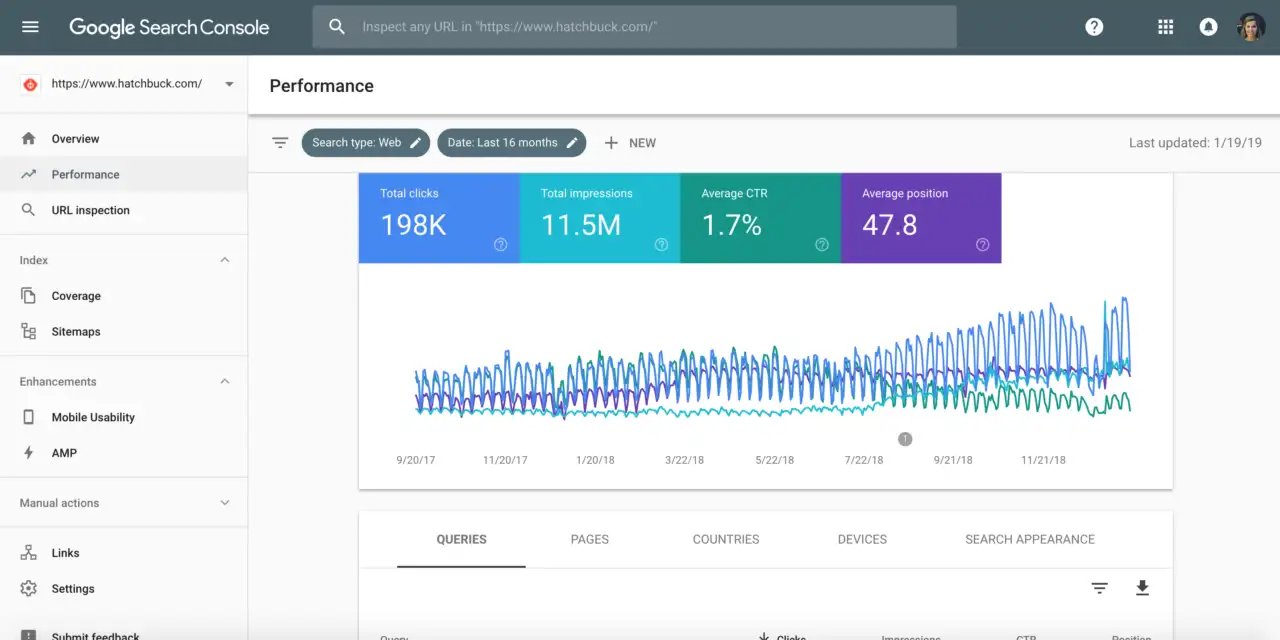
Tools for tracking your Search Engine Positions
The biggest and best tool for tracking search engine positions will be the search engines themselves.
Google offers Google Search Console, Bing offers Bing Webmasters etc.
These tools will show you the actual ranking data in real time.
There are some other tools that do offer some extra benefits however:
- SEMRush - An all in one SEO and Marketing Tool, SEMRush has the functionality to track the positions over time.
- AHRefs - AHRefs is also another all in one SEO tool that focuses in a more pure sense on SEO (and not marketing, brand awareness etc.)
There is a big benefit in tracking your positions over time. Now, of course you could go in to Google Search Console daily (or weekly) and download your positions against their respective keywords and that would show you how you are doing. Using a tool like SEMRush or AHRefs does take the effort out of that though.
Leveraging Analytics for Search Positioning
But why track your search engine positions at all? If you don't, how else will you know what is working and what isn't?
Whilst there is a lot of science in SEO, there's also a lot of art and black magic. Track what you've done, look at the results of your pages in the SERP rankings and them try to replicate that across other pages.
Using tools such as Google Analytics can help you understand the usage of your sites for users. How long is the average user session? How many pages does the average user visit? Does the average user return, or are most of your users new users. All of these metrics can help you understand the "user journey". When we understand the user journey, we can improve.
In God we trust. All others, bring data.
The sites that don't evolve based on feedback and data will die. You need to try things out, see what works, see what doesn't and replicate the good whilst deprecating the bad.
What are some key metrics to track?
- Average Session Time per page. How long does each person that hits your page actually spend on your page. You can use Google Analytics for this.
- Scroll Depth per page. How far down does the average user get before stopping. This may highlight that you need to restructure your page, or even that you need to be more engaging. You can use Heatmap tools Hotjar, which through some Javascript can monitor things such as scroll depth, but also clicks, rage clicks, time spent per section etc.
- Search Engine Rankings Positions. This is the main one (don't know why I didn't put it first). Without knowing how your rankings change after making changes, you can't know what is working and what isn't. Either do this the cheap but accurate way of using Google Search Console and periodically downloading the rankings positions so you can plot them over time, or use a tool like SEMRush or AHRefs to track them for you.
Improving User Experience (UX)

What makes a good user experience?
For me, it's a fast loading page that is not too "full", gives effective "eye breaks", no flashing images, no moving adverts etc. I think we all know a bad website and bad user experience when we see one. Think of those gambling sites that have Ads in every pixel of the screen and you have to actually search for the real content.
User Experience matters a lot in Search Engine Positioning. If you have a good user experience, Google gets those signals. They see that once people visit your site, they stay, they learn and then they don't go back to Google and continue searching. These are positive signs that your web page has solved the users query.
Of course you need good content, but user experience (UX) is just as important.
Common Pitfalls in SEO Positioning
Let's look at some common pitfalls in SEO Positioning.
Keyword Choice
You've hopefully already got a pretty solid keyword strategy, but if you haven't you should get one. Within that strategy I'd imagine you've considered the competitiveness of that Keyword as well as the nature and intent of it. SEO positioning is no different. Choosing the wrong keyword when trying to raise the rankings of your page will ultimately fail. You'll probably learn some lessons on the way, but unlikely in a good way.
Look for those long tail keywords and low competition keywords. Use a tool like SEMRush or AHRefs to get an understanding of where you site ranks in terms of authority, and check out the "keyword difficulty" of some of the keywords you already rank for. Remember, these metrics from these tools are really just a guide.
Thin or Duplicate Content

Trying to position a page higher in the rankings, when the page itself is not useful is a hard task. If your competitors are writing 3,000 words to fully cover a topic and you are trying to rank a page with 500 words of fluff, you aren't going to stand a chance. Write good quality content that fully covers the topic at hand.
Bad On Page SEO
One of the first things you need to do when working on Search Engine Positioning is to ensure your on Page SEO is on point. Use tools like RankReady to write your articles, to ensure you are hitting your on page SEO targets, as well as including those well needed semantically related keywords.
Ignoring Technical SEO
You need to be running tools that analyze your technical SEO. ScreamingFrog is a great and free tool (albeit not too beginner friendly) that you can run over your site to pick up on many things, such as:
- Broken Links
- Large Images
- Missing Meta Data
- Slow load times
The list goes on. If your website is full of these errors, chances are that Google won't give you much crawl budget and also won't rank you very highly.
Not enough Backlinks
Backlinks are a key trust signal to Google and other Search Engines. They tell the company that other people value the content that you have created. If a large corporation like the BBC, TechCrunch, Reuters etc has given you their seal of approval by linking to your web page, Google will understand that there must be something good there.
The higher the keyword difficulty, generally the more high quality backlinks you'll need.
How to recover from a drop in Search Rankings
I'll be blunt here. When you change things, sometimes they won't work.
If you are trying to break the stasis, there is a chance that you'll make things worse before you make them better.
To recover from this, you need to remember what you've done. You need to understand the link between your actions, and the results. Keep a good track of your changes and monitor the metrics closely.
Sometimes, changes in rankings are beyond your control. Another site may have started to target the same keyword and they may be much bigger than you. Google may have released a core update and changed how it ranks pages. For those things, you need to keep up on the SEO trends and make sure you are acting accordingly.
Tips for maintaining long-term SEO Health
You need to build in SEO health checking in to your schedule. You can do this manually by setting a weekly alarm and going to do some of the checks mentioned on this page, or you can use tooling to schedule weekly reports.
ScreamingFrog and many other tools allow you to schedule site audits, and you will get the report emailed to you. Check these thoroughly and make sure you fix all of the high and medium priority items.
Conclusion: Mastering Search Engine Positioning
Search Engine Positioning is one of the SEO strategies you need to have in your back pocket.
When you break it down, it's fairly simple:
- Identify a page you want to rank higher
- Do a round of good content optimization
- Look at core web vitals and mobile optimization
- Ensure your keyword or new keyword are attainable by your website
- Gather more high quality backlinks to the page.
If you do all of this successfully, the traffic will follow.
One final comment:
The SEO world is ever evolving. Make sure you are keeping up to date with all of the latest SEO trends, what is working and what's not. What works today, might not work tomorrow.